Blockchain is a revolutionary digital technology designed to securely record, store, and share information across a distributed network. Unlike traditional, centralized databases, blockchain is not controlled by any single entity. Instead, it functions as a decentralized, peer-to-peer ledger that provides transparency, immutability, and strong security. Let’s see How Blockchain Works?
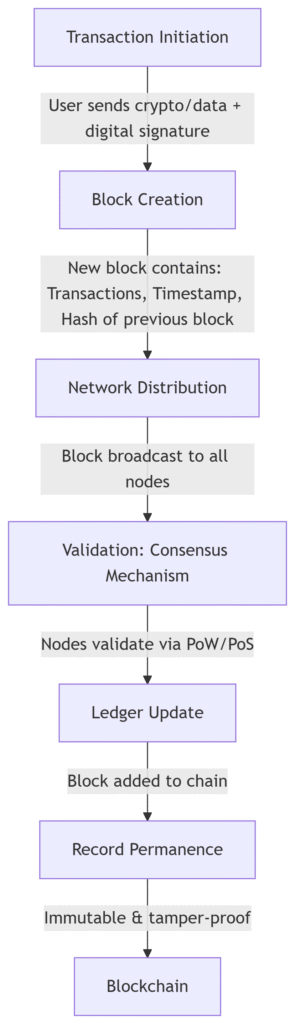
Blockchain operates as a decentralized digital ledger made up of a series of linked “blocks,” each containing groups of transactions. Here’s how the process works:
- Transaction Initiation
A user creates a digital transaction—such as sending cryptocurrency or exchanging data—which is digitally signed for authenticity. - Block Creation
This transaction, along with others, is grouped into a new block. The block records the data, a timestamp, a digital signature, and a reference (hash) linking it to the previous block. - Network Distribution
The new block is broadcast to all nodes (computers) participating in the blockchain network. - Validation (Consensus Mechanism)
The network uses a consensus protocol (e.g., Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to confirm that the transactions within the block are valid. Most nodes must approve the block for it to be added. - Ledger Update
Upon validation, the block is permanently added to the blockchain on every node, making the record tamper-resistant. - Record Permanence
Once a block is added, altering data would require consensus from the majority of the network, making retroactive changes nearly impossible.
This process ensures that every transaction is securely recorded, transparent to participants, and resistant to tampering or unauthorized modification.

Pingback: What is Blockchain? - All About Blockchain