Blockchain is like a digital notebook that keeps track of transactions in a secure and transparent way. Instead of one person or company controlling it, many computers (called nodes) work together to maintain it.
•A distributed, immutable ledger recording transactions across a network of nodes.
How Does Blockchain Work?
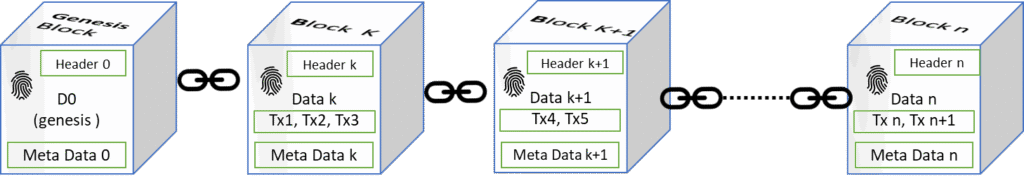
Imagine a chain of blocks where each block contains a list of transactions (like money transfers, contracts, or records). Once a block is full, it gets added to the chain in a way that makes it nearly impossible to change old records.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Transaction Happens – Someone sends money or data.
- Verification – Computers in the network check if the transaction is valid.
- Block Creation – Verified transactions are grouped into a block.
- Adding to the Chain – The block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain.

For detailed explanation of How Does Blockchain Work? read this article.
Why is Blockchain Special?
- Decentralized – No single bank or company controls it.
- Transparent – Everyone can see transactions (but not necessarily personal details).
- Secure – Once data is recorded, it’s very hard to change.
- No Middlemen – Transactions happen directly between people.
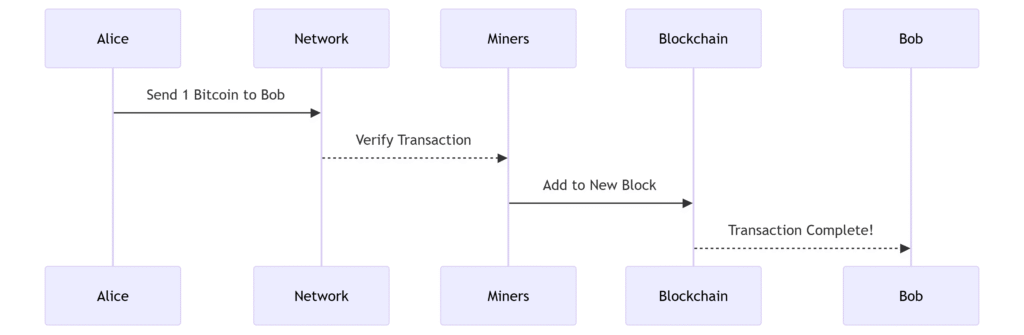
Example: Sending Bitcoin
If Alice sends Bob 1 Bitcoin:
- The transaction is broadcast to the network.
- Miners (special nodes) verify it.
- Once confirmed, it’s added to a block.
- The block joins the blockchain, and Bob receives his Bitcoin.
Where is Blockchain Used?
- Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum)
- Smart Contracts (Self-executing agreements)
- Supply Chain Tracking (Checking where products come from)
- Voting Systems (Secure and transparent elections)
Final Thought
Blockchain is like a super-secure, shared digital ledger that removes the need for trust in a single authority. It’s changing how we handle money, contracts, and data!

