Introduction: The Blockchain Scalability Problem
Blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum face a fundamental challenge: the scalability trilemma—balancing decentralization, security, and scalability. As adoption grows, networks become congested, leading to:
- Slow transactions (Bitcoin: 7 TPS, Ethereum: 15-30 TPS)
- High gas fees (Ethereum fees can exceed $50 during peak times)
- Limited throughput (Struggles with mass adoption)
To solve this, developers have created scaling solutions, primarily:
- Layer 1 Scaling (Sharding, Consensus Upgrades)
- Layer 2 Scaling (Rollups, Sidechains, State Channels)
This guide breaks down the two most promising approaches: Sharding and Rollups.
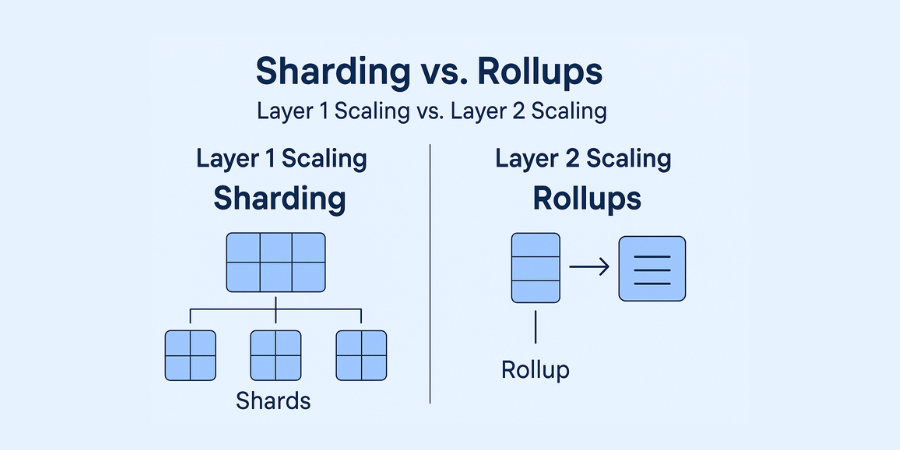
1. Layer 1 Scaling: Sharding
What Is Sharding?
Sharding is a database partitioning technique adapted for blockchains. Instead of every node processing every transaction, the network is split into smaller segments (“shards”), each handling a portion of transactions in parallel.
How Sharding Works
- Network Splitting → The blockchain is divided into multiple shards (e.g., 64 in Ethereum 2.0).
- Parallel Processing → Each shard processes its own transactions and smart contracts.
- Cross-Shard Communication → Special protocols ensure shards can interact securely.
Pros & Cons of Sharding
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increases throughput significantly | Complex to implement |
| Maintains decentralization | Cross-shard communication challenges |
| Reduces node storage requirements | Security risks if a shard is compromised |
Real-World Example:
- Ethereum 2.0 plans to implement sharding post-merge (expected 2023-2024).
2. Layer 2 Scaling: Rollups
What Are Rollups?
Rollups are Layer 2 solutions that process transactions off-chain and then post compressed data back to the main blockchain (Layer 1).
Types of Rollups
| Type | How It Works | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Optimistic Rollups | Assumes transactions are valid (fraud proofs used if challenged) | Lower fees, slower withdrawals |
| ZK-Rollups (Zero-Knowledge) | Uses cryptographic proofs (SNARKs/STARKs) for instant verification | Faster, more secure, but computationally heavy |
How Rollups Improve Scalability
- Bundling Transactions → Thousands of transactions are processed off-chain.
- Compressed Data → Only proof/summary is posted to Layer 1.
- Inherits Security → Still anchored to Ethereum/Bitcoin.
Pros & Cons of Rollups
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 100-1000x cheaper than Layer 1 | Requires trust in operators (Optimistic) |
| Faster transactions | ZK-Rollups need complex cryptography |
| Compatible with existing apps | Withdrawal delays (Optimistic) |
Real-World Examples:
- Optimism & Arbitrum (Optimistic Rollups)
- zkSync & StarkNet (ZK-Rollups)
3. Sharding vs. Rollups: Key Differences
| Feature | Sharding (Layer 1) | Rollups (Layer 2) |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Modifies blockchain itself | Built on top of blockchain |
| Security Model | Inherits base layer security | Depends on rollup type (ZK = trustless) |
| Speed Boost | ~10-100x | ~100-1000x |
| Adoption Status | Still in development (Ethereum 2.0) | Live (Arbitrum, zkSync) |
Which Is Better?
- Rollups → Faster to deploy, already working today.
- Sharding → Long-term solution but more complex.
- Best Case → Combined approach (Ethereum plans to use both).
4. Other Scaling Solutions
A. Sidechains (Polygon, Ronin)
- Independent blockchains with their own consensus.
- Pros: Fast, cheap | Cons: Less secure than L1.
B. State Channels (Lightning Network)
- Off-chain payment channels (e.g., Bitcoin Lightning Network).
- Pros: Instant transactions | Cons: Limited to payments.
C. Plasma Chains
- Child chains that periodically commit to Ethereum.
- Pros: Scalable | Cons: Complex withdrawals.
5. The Future of Blockchain Scaling
Ethereum’s Roadmap
- The Merge (PoS) → Completed (2022)
- Surge (Rollups + Sharding) → Expected 2023-2024
- Verge, Purge, Splurge → Further optimizations
Emerging Innovations
- Modular Blockchains (Celestia)
- ZK-EVMs (Scroll, Polygon zkEVM)
- Danksharding (Ethereum’s sharding upgrade)
Conclusion
Blockchain scaling is essential for mass adoption, and solutions like sharding and rollups are leading the way:
- Sharding improves Layer 1 throughput by parallel processing.
- Rollups boost efficiency by moving computation off-chain.
While rollups are already live (Arbitrum, zkSync), sharding remains in development. The future likely involves hybrid solutions combining both approaches.